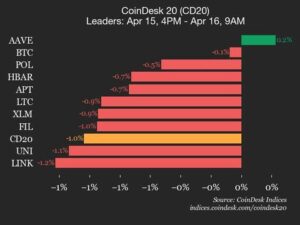
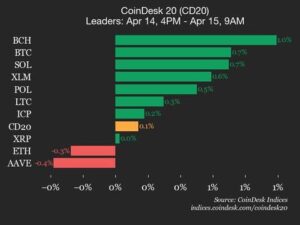
In the world of cryptocurrency, staking has emerged as a popular method for individuals to earn rewards by participating in the validation process of specific cryptocurrencies. This concept is rooted in a consensus mechanism known as «proof of stake,» which allows holders to contribute their coins to help maintain the blockchain’s integrity while potentially earning returns in the process.
Understanding Crypto Staking
At its core, staking enables users to lock up a portion of their cryptocurrency holdings to support network operations, such as transaction verification. Participants, known as validators, are rewarded with new coins for their contributions. Unlike traditional mining, which relies on complex mathematical problem-solving, proof of stake selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to «stake.» This method is considered more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly than the proof-of-work model used by Bitcoin.
How Does Staking Work?
When you stake your cryptocurrency, you essentially lend it to the network, which uses your contribution to secure transactions. The blockchain rewards you with additional coins proportional to your stake. The selection of validators is semi-random and takes into account factors such as the size of the stake and how long it has been held. However, there are risks involved, including market volatility and potential lock-up periods where your assets may be inaccessible.
Proof of Stake Explained
Proof of stake is a consensus mechanism that serves as an alternative to the mining process used in proof-of-work systems. In a proof of stake system, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked. This streamlined approach reduces the need for extensive computational resources, resulting in faster transaction validation and lower energy consumption.
Popular Cryptocurrencies Utilizing Proof of Stake
While not all cryptocurrencies employ staking, several notable ones do, including:
- Cardano (ADA)
- Solana (SOL)
- Avalanche (AVAX)
These currencies leverage the proof-of-stake model to enhance their operational efficiency and security.
Getting Started with Staking
For those interested in staking, there are several options available. You can either stake directly through a cryptocurrency exchange, which simplifies the process by handling much of the operational work, or join a staking pool. A staking pool allows multiple participants to combine their resources, increasing the chances of earning rewards while sharing the responsibilities of managing the staking process.
Advantages of Staking
Engaging in crypto staking can offer several benefits, such as:
- Potential for high returns, varying by cryptocurrency.
- The opportunity to support projects you believe in by contributing to their functionality.
- No need for specialized equipment or extensive technical knowledge.
Risks Associated with Staking
Despite its advantages, staking carries inherent risks. These include:
- Price volatility, which can significantly affect the value of your staked assets.
- Lock-up periods that may prevent you from accessing your funds for a specified duration.
- Security risks when entrusting your cryptocurrency to exchanges or nodes for staking purposes.
Conclusion
Staking presents a unique way to earn rewards while contributing to the security and efficiency of blockchain networks. However, it is essential to weigh the potential benefits against the risks involved. For those looking to explore the world of cryptocurrencies, understanding staking is a key step in navigating the evolving landscape of digital assets.